
Introduction
Definition and Overview
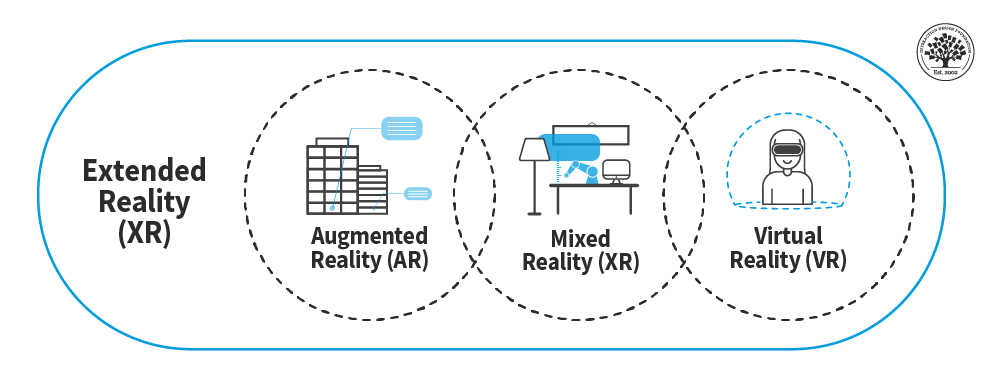
- Explanation of Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Extended Reality (XR)
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR creates a fully immersive digital environment that users can interact with through specialized equipment like headsets. It’s designed to replace the real world with a simulated one, providing experiences that can range from games to virtual tours.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR overlays digital information and graphics onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their physical environment. This is commonly experienced through smartphones and AR glasses, which add interactive elements to real-world scenes.
- Extended Reality (XR): XR is an overarching term that encompasses all immersive technologies, including VR, AR, and Mixed Reality (MR). It represents the spectrum of digital experiences that blend or replace reality with virtual elements.
- Brief History and Evolution of These Technologies
- Early Concepts: The roots of VR and AR can be traced back to the mid-20th century with the development of early simulation and display technologies.
- Advancements: VR gained momentum in the 1980s and 1990s with advancements in computing power and graphics. AR started to take shape with the development of wearable computing and mobile technology in the 2000s.
- Modern Era: The 2010s and 2020s saw rapid advancements in VR and AR, driven by consumer interest, improved hardware, and software innovations. XR emerged as a unified concept to describe the full range of immersive technologies.
Importance of Technology in Modern Life
- How These Technologies Are Reshaping Our Everyday Experiences
- Enhanced Interaction: VR and AR provide new ways to interact with digital content, making activities like gaming, shopping, and learning more engaging and interactive.
- Improved Accessibility: These technologies offer new opportunities for people with disabilities, such as virtual simulations for physical therapy or AR applications that provide real-time assistance.
- The Growing Accessibility and Relevance of VR, AR, and XR for Non-Tech Individuals
- User-Friendly Devices: Modern VR and AR devices have become more affordable and user-friendly, making them accessible to a broader audience.
- Diverse Applications: From education and healthcare to entertainment and retail, VR and AR are increasingly integrated into various aspects of daily life, offering practical solutions and enhancing experiences for people of all backgrounds.
Intended Audience
- Who Will Benefit from Learning About These Technologies
- General Public: Individuals curious about how VR, AR, and XR might impact their personal and professional lives.
- Educators and Students: Those interested in incorporating these technologies into teaching and learning processes.
- Industry Professionals: Those in sectors such as healthcare, retail, and entertainment who are looking to understand how these technologies can be leveraged for their industries.
- Tech Enthusiasts and Innovators: Individuals and groups exploring new technological frontiers and seeking to understand the future of immersive tech.
- Immersive Digital Environments and Experiences
- Immersive Environments: Virtual Reality (VR) refers to technology that creates a simulated, three-dimensional environment that users can explore and interact with. Unlike traditional screens, VR completely envelops the user in a digital world, often using a VR headset that includes built-in sensors and displays to track head movements and adjust the visuals accordingly.
- Interactive Experiences: VR experiences can be highly interactive, allowing users to manipulate objects, navigate spaces, and engage with simulations as if they were physically present. This immersion is achieved through a combination of visual, auditory, and sometimes haptic (touch) feedback, creating a convincing sense of presence in a virtual world.
- Gaming
- Enhanced Immersion: VR gaming provides players with a more immersive and interactive experience compared to traditional gaming setups. Players can physically move and interact with the game world, making the gameplay more engaging and realistic.
- Education
- Interactive Learning: VR can simulate complex environments and scenarios, making it an effective tool for education. For example, VR can transport students to historical events, explore the human anatomy, or practice skills in a safe, controlled environment.
- Virtual Tourism
- Exploring Remote Destinations: VR allows users to experience virtual tours of destinations, museums, and landmarks without leaving their homes. This can be particularly beneficial for those unable to travel or those seeking to explore new places before visiting in person.
- Remote Work
- Virtual Collaboration: VR can facilitate remote work by creating virtual meeting spaces where team members can collaborate as if they were in the same room. This can enhance communication and teamwork, especially for global or distributed teams.
Who Should Learn About VR?
- Educators
- Integration into Curriculum: Teachers and educators can leverage VR to enhance the learning experience, making lessons more engaging and interactive through virtual field trips, simulations, and interactive content.
- Content Creators
- Developing VR Experiences: Writers, designers, and developers can create immersive VR content, from games and educational programs to virtual exhibitions and interactive stories.
- Gamers
- Exploring New Gaming Horizons: Gamers interested in experiencing new forms of interactive entertainment can benefit from understanding VR technologies, which offer a novel and immersive approach to gaming.
- Healthcare Professionals
- Therapeutic and Training Applications: VR can be used in healthcare for various purposes, including pain management, physical rehabilitation, and medical training. Professionals in this field can use VR to enhance patient care and training programs.
This section provides a clear explanation of what Virtual Reality (VR) is, how it is used in everyday applications, and who might benefit from learning about it. It highlights the diverse potential of VR and its relevance across different fields.

Understanding Augmented Reality (AR)
Detailed Definition
- Enhancing the Real World with Digital Overlays
- Digital Overlays: Augmented Reality (AR) refers to technology that overlays digital information—such as images, text, and animations—onto the real world. This enhancement allows users to interact with both physical and digital elements simultaneously through devices like smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses.
- Real-Time Interaction: AR integrates digital content in real-time with the physical environment, enriching the user’s perception without completely replacing the real world. This integration can provide contextually relevant information or interactive elements that complement the real-world experience.
Everyday Applications
- Mobile Gaming
- Interactive Experiences: AR games, such as Pokémon Go, blend the digital and physical worlds by placing virtual characters and objects in real-world locations. Players interact with these virtual elements as they move around their actual environment, creating an immersive and engaging experience.
- Navigation
- Enhanced Directions: AR applications like Google Maps use AR to overlay directional arrows and information on the live camera feed of a mobile device, helping users navigate more intuitively by providing real-time guidance within their surroundings.
- Shopping
- Virtual Try-Ons: Retailers such as IKEA use AR to allow customers to visualize how furniture and other products will look in their own homes before making a purchase. Apps like IKEA Place let users place virtual items in their real-world space to see how they fit and match with existing décor.
Who Should Learn About AR?
- Retail Professionals
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Retailers can use AR to offer interactive shopping experiences, improving customer engagement and satisfaction through virtual try-ons, product visualizations, and immersive advertisements.
- Marketing Teams
- Innovative Campaigns: Marketers can leverage AR to create unique and memorable promotional campaigns, integrating interactive elements that capture consumer attention and enhance brand experiences.
- Mobile App Developers
- Creating AR Applications: Developers can explore AR technology to build innovative mobile apps that provide users with enhanced functionalities and experiences, ranging from games to productivity tools.
- Educators
- Interactive Learning Tools: Educators can use AR to create interactive learning materials that bring subjects to life, such as visualizing complex scientific concepts or historical events in a more engaging way.
- The General Public
- Enhanced Daily Interactions: Individuals interested in new technology and digital enhancements can benefit from understanding AR, which has practical applications in various aspects of everyday life, including navigation, entertainment, and shopping.
This section provides a thorough understanding of Augmented Reality (AR), detailing how it enhances the real world with digital elements, its applications in daily life, and the diverse audience that can benefit from learning about AR.
Exploring Extended Reality (XR)
Definition and Scope
- The Umbrella Term Encompassing VR, AR, and Mixed Reality (MR)
- Extended Reality (XR): XR is a comprehensive term that encompasses all immersive technologies, including Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). It represents a continuum of digital experiences where the physical and digital worlds interact and overlap in varying degrees.
- Mixed Reality (MR): MR combines elements of both VR and AR to create environments where physical and digital objects coexist and interact in real-time. Unlike AR, which simply overlays digital information, MR allows for more complex interactions between the virtual and real worlds, often requiring advanced hardware and software.
Applications in Various Industries
- Healthcare
- Medical Training and Simulations: XR can be used for realistic training simulations, such as surgical procedures and patient care scenarios, helping medical professionals practice skills in a risk-free environment.
- Therapeutic Uses: XR technologies are increasingly used for therapeutic purposes, including pain management, exposure therapy, and rehabilitation, providing immersive environments that aid in physical and psychological treatment.
- Real Estate
- Virtual Tours and Property Visualization: XR allows potential buyers to explore properties virtually, offering immersive tours and 3D visualizations that help them better understand the space and make informed decisions.
- Architectural Design: Architects and builders use XR to visualize and interact with building designs in real-time, making it easier to assess and modify plans before construction begins.
- Education
- Immersive Learning Environments: XR can transform education by creating interactive and engaging learning experiences. For instance, students can explore historical events, conduct virtual science experiments, or practice language skills in simulated environments.
- Skill Development: XR offers practical training tools for various skills, including vocational training and professional development, providing hands-on practice in a controlled virtual setting.
- Entertainment
- Immersive Experiences: XR enhances entertainment through interactive and immersive experiences, such as VR concerts, AR-based games, and interactive storytelling. These applications offer new ways to engage audiences and create memorable experiences.
- Content Creation: XR allows content creators to develop innovative and interactive media, pushing the boundaries of traditional entertainment formats and exploring new creative possibilities.
Who Should Learn About XR?
- Industry Professionals
- Adapting to New Technologies: Professionals across various industries, from healthcare to real estate, can benefit from understanding XR to stay competitive and leverage these technologies for innovation and efficiency.
- Innovators
- Exploring New Opportunities: Innovators interested in pushing the boundaries of technology and creating new applications can explore XR to develop cutting-edge solutions and products.
- Educators
- Enhancing Teaching Methods: Educators can use XR to enrich teaching methods, offering students interactive and immersive learning experiences that can improve engagement and comprehension.
- Technologists
- Advancing Technology: Technologists and developers working on emerging technologies should be familiar with XR to contribute to its advancement and create new applications that leverage its full potential.
This section provides an overview of Extended Reality (XR), including its definition and scope, its applications across different industries, and the diverse audience that can benefit from learning about XR. It highlights how XR represents a broad spectrum of immersive technologies and the various ways it can be applied to enhance and innovate different fields.
Practical Examples Across Industries
Healthcare
- Virtual Surgeries
- Training and Simulation: Surgeons can use VR to simulate complex procedures, allowing them to practice and refine their skills in a risk-free environment. VR can also assist in planning surgeries by providing a detailed 3D model of the patient’s anatomy.
- Remote Assistance: Surgeons can use VR to receive real-time guidance from experts during actual surgeries, enabling collaborative and precise interventions from remote locations.
- AR in Diagnostics
- Enhanced Imaging: AR can overlay digital information onto diagnostic images (e.g., X-rays, MRIs), helping radiologists and doctors identify anomalies more effectively. This integration can provide a clearer view of the problem areas and assist in diagnosis.
- Interactive Tools: AR can offer interactive tools for medical professionals, such as visualizing the internal structure of the body or guiding procedures with augmented annotations and overlays.
- Mental Health Therapy Using VR
- Exposure Therapy: VR can be used for exposure therapy, helping patients confront and manage phobias, anxiety, and PTSD by immersing them in controlled virtual environments.
- Relaxation and Stress Relief: VR environments designed for relaxation and mindfulness can assist in stress management and mental well-being, providing calming and immersive experiences.
Education
- Immersive Learning Environments
- Virtual Field Trips: VR enables students to experience historical events, explore distant planets, or visit ancient civilizations, making learning more engaging and interactive.
- Simulated Labs: VR can simulate scientific experiments and laboratory environments, allowing students to conduct experiments and learn practical skills in a safe, virtual setting.
- Virtual Classrooms
- Remote Learning: VR can create virtual classrooms where students and teachers interact as if they were physically present, facilitating remote education with a sense of presence and engagement.
- Collaborative Projects: Virtual classrooms enable students to work on group projects and collaborate with peers from around the world, enhancing learning through interactive and shared experiences.
- AR in Textbooks
- Interactive Content: AR can enhance traditional textbooks by overlaying interactive elements, such as 3D models, videos, and animations, providing a richer and more immersive learning experience.
- Visualizing Concepts: AR can help students better understand complex concepts by visualizing abstract ideas and processes in a more tangible and interactive manner.
Retail
- Virtual Fitting Rooms
- Try-Ons at Home: AR allows customers to virtually try on clothing and accessories using their smartphones or AR mirrors in stores, helping them see how items will look on them without physically trying them on.
- Personalized Recommendations: Virtual fitting rooms can use AR to offer personalized style recommendations based on the user’s preferences and previous choices.
- AR-Based Shopping Experiences
- Product Visualization: AR can enable customers to visualize how products will fit or look in their homes before making a purchase, such as seeing how furniture fits in a room or how paint colors look on walls.
- Interactive Storefronts: Retailers can use AR to create interactive storefronts, where customers can scan products with their smartphones to access detailed information, reviews, and special offers.
Entertainment and Gaming
- VR Gaming Experiences
- Immersive Gameplay: VR gaming offers an immersive experience where players can physically interact with the game world, enhancing the realism and engagement of the gameplay.
- New Genres: VR has introduced new genres and gameplay mechanics that leverage the technology’s ability to create interactive and spatially aware environments.
- Immersive Movies
- 360-Degree Films: VR allows viewers to experience movies in a 360-degree format, placing them inside the film’s environment and enabling a more interactive and engaging viewing experience.
- Interactive Stories: Some films and storytelling experiences use VR to allow viewers to make choices and influence the storyline, creating a more personalized and interactive narrative.
- Interactive Storytelling
- Narrative Experiences: VR and AR can create interactive storytelling experiences where users actively participate in the story, making decisions and interacting with characters and environments.
- Live Performances: XR technologies can enhance live performances, such as concerts and theater, by integrating virtual elements and interactive components into the shows.
This section provides practical examples of how VR, AR, and XR are applied across various industries, highlighting their transformative impact on healthcare, education, retail, and entertainment. It showcases the diverse applications and benefits of these technologies, illustrating their potential to enhance and innovate different fields.
Evolution and Current State of VR, AR, and XR
Technological Advancements
- Key Milestones in the Development of VR, AR, and XR
- Early Beginnings
- 1960s-1980s: The foundations of VR and AR were laid with early experiments in computer-generated imagery and simulation. Notable milestones include the development of the first head-mounted display by Ivan Sutherland and the early concept of AR by Tom Caudell.
- 1990s-2000s: VR technology saw significant advancements with the introduction of more sophisticated VR systems like the Virtuality arcade machines and the rise of AR in military and industrial applications. The late 1990s also marked the beginning of commercial VR gaming with products like the Sega VR headset.
- 2010s: The advent of consumer-grade VR and AR devices transformed the landscape. Oculus Rift’s Kickstarter campaign in 2012 and the subsequent release of the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR in the mid-2010s brought VR into the mainstream. AR saw significant growth with the release of Pokémon Go in 2016, showcasing the potential of AR in mobile gaming.
- 2020s-Present: XR technologies have continued to evolve with advancements in hardware and software. Key developments include the integration of AR into smartphones and wearables, the rise of Mixed Reality (MR) with devices like Microsoft HoloLens and Meta Quest Pro, and ongoing improvements in immersive experiences and interactivity.
- Early Beginnings
Current Market and Adoption Rate
- Overview of the Current Landscape
- VR Market
- Growth and Trends: The VR market has experienced significant growth, driven by advancements in hardware, software, and content creation. The market includes a diverse range of applications, from gaming and entertainment to education and healthcare.
- Key Players: Major companies in the VR space include Meta (formerly Facebook), Sony, HTC, and Valve. These companies continue to innovate and expand their VR offerings, contributing to the overall growth of the industry.
- AR Market
- Expansion and Integration: The AR market has seen widespread adoption, particularly in mobile applications and retail. AR has become a key component of marketing strategies and customer engagement, with applications in virtual try-ons, interactive ads, and enhanced shopping experiences.
- Key Players: Leading companies in the AR space include Apple, Google, Microsoft, and Snap Inc. These companies are investing in AR technology and developing new applications to enhance user experiences and expand market reach.
- XR Market
- Unified Growth: The XR market represents the convergence of VR, AR, and MR technologies. This sector is growing rapidly as companies explore new ways to integrate and utilize these technologies for various applications, including immersive entertainment, remote collaboration, and training.
- Key Developments: Recent advancements in XR include improved hardware capabilities, such as higher resolution displays and better tracking, as well as more sophisticated software solutions that enable seamless integration of virtual and physical elements.
- VR Market
- Adoption by Different Industries
- Healthcare: Adoption of VR and AR in healthcare continues to grow, with applications in medical training, surgery simulation, and mental health therapy. The industry is leveraging these technologies to improve patient care, enhance medical education, and streamline clinical procedures.
- Education: Educational institutions are increasingly incorporating VR and AR into their curricula to provide interactive and immersive learning experiences. These technologies are used for virtual field trips, simulated labs, and interactive textbooks, enhancing student engagement and understanding.
- Retail: Retailers are adopting AR to enhance the shopping experience through virtual try-ons, product visualization, and interactive storefronts. This adoption is driven by the desire to offer innovative and convenient shopping solutions to customers.
- Entertainment and Gaming: The gaming industry is a major driver of VR and AR adoption, with new games and experiences pushing the boundaries of interactive entertainment. Additionally, XR technologies are being used to create immersive films, interactive storytelling, and live performances.
This section outlines the evolution of VR, AR, and XR technologies, highlighting key milestones and advancements. It also provides an overview of the current market and adoption rates across various industries, illustrating how these technologies are shaping and transforming different fields.

Devices Available Today
VR Headsets
- Oculus Rift
- Overview: One of the pioneering consumer VR headsets, Oculus Rift offers a high-quality immersive experience with precise tracking and a wide field of view.
- Key Features: Includes a high-resolution display, integrated headphones, and accurate motion tracking. The Rift is known for its extensive library of VR games and applications.
- Current Status: The Oculus Rift has been succeeded by the Oculus Quest series, but its legacy continues to influence VR development.
- HTC Vive
- Overview: The HTC Vive is a leading VR headset known for its room-scale tracking capabilities, providing an immersive experience with physical movement.
- Key Features: Features external base stations for precise tracking, high-resolution displays, and a wide range of accessories. It supports a variety of VR applications, including games and professional simulations.
- Current Status: HTC continues to update and expand its Vive product line with new models and enhancements.
- PlayStation VR
- Overview: Designed for use with PlayStation consoles, PlayStation VR offers an accessible VR experience for gamers using Sony’s gaming ecosystem.
- Key Features: Integrates with PlayStation 4 and PlayStation 5, featuring a headset with built-in headphones, a PlayStation Camera for tracking, and a library of exclusive VR games.
- Current Status: PlayStation VR has been updated with the PlayStation VR2 for the PS5, offering improved visuals and new features.
AR Glasses
- Microsoft HoloLens
- Overview: HoloLens is a leading Mixed Reality (MR) headset that overlays digital information onto the real world, designed primarily for enterprise use.
- Key Features: Features spatial mapping, gesture controls, and voice commands, allowing users to interact with holographic content in a natural and intuitive way.
- Current Status: The HoloLens 2 has improved on its predecessor with better comfort, higher resolution, and enhanced interaction capabilities.
- Google Glass
- Overview: Google Glass is a lightweight, wearable AR device designed for hands-free use of digital information and applications.
- Key Features: Includes a small display that projects information into the user’s field of view, voice commands, and a touchpad for navigation. It is used in various applications, including enterprise and healthcare.
- Current Status: The original consumer version was discontinued, but Google Glass has evolved into a tool for enterprise applications.
- Magic Leap
- Overview: Magic Leap is a pioneering AR headset that aims to create immersive and interactive experiences by blending digital content with the physical world.
- Key Features: Features advanced spatial computing, high-fidelity visualizations, and a wide field of view. It is designed for both enterprise applications and creative development.
- Current Status: Magic Leap continues to develop and refine its technology, focusing on applications in various industries.
Mobile AR
- AR Apps and Experiences on Smartphones and Tablets
- Overview: Mobile AR utilizes the cameras and sensors of smartphones and tablets to provide augmented experiences. This category includes a wide range of applications from gaming to practical utilities.
- Popular Apps:
- Pokémon Go: A groundbreaking AR game that overlays Pokémon characters onto real-world environments, allowing players to catch and interact with them.
- IKEA Place: An app that lets users visualize how furniture will look in their homes by overlaying 3D models of products onto live camera feeds.
- Google Lens: An AR tool that provides information about objects and text captured through the camera, enhancing search and interaction with the physical world.
- Current Status: Mobile AR continues to evolve with advancements in smartphone technology, offering increasingly sophisticated and immersive experiences.
XR Devices
- Meta Quest Pro
- Overview: Meta Quest Pro (formerly Oculus Quest Pro) is a cutting-edge XR device that blends VR and AR capabilities for a comprehensive immersive experience.
- Key Features: Includes high-resolution displays, advanced tracking, and mixed reality functionality, allowing users to interact with both virtual and real-world elements seamlessly.
- Current Status: Continues to be at the forefront of XR innovation, providing users with versatile and immersive experiences across various applications.
- Varjo XR-3
- Overview: The Varjo XR-3 is a high-end XR headset designed for professional use, offering exceptional visual fidelity and mixed reality capabilities.
- Key Features: Features ultra-high resolution displays, precise tracking, and advanced mixed reality functionalities, making it suitable for industries such as design, training, and simulation.
- Current Status: The Varjo XR-3 is known for its premium quality and is used in various professional and industrial applications.
- Devices That Blend AR and VR
- Overview: Several devices are designed to seamlessly integrate AR and VR functionalities, providing users with flexible and immersive experiences.
- Examples: Devices like the Meta Quest Pro and Varjo XR-3 offer a combination of VR immersion and AR interactivity, allowing users to switch between or blend virtual and physical worlds.
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the current devices available for VR, AR, and XR experiences, highlighting key products and their features. It covers a range of devices from consumer-oriented VR headsets and AR glasses to mobile AR applications and advanced XR devices.

The Future of VR, AR, and XR
Emerging Trends
- Predictions for the Next Decade in VR, AR, and XR Development
- Enhanced Immersion and Interactivity
- Improved Hardware: Expect significant advancements in hardware, including higher resolution displays, more accurate motion tracking, and more comfortable and lightweight headsets. These improvements will enhance the overall immersive experience and reduce motion sickness.
- Haptic Feedback: Advances in haptic technology will provide more tactile and realistic sensations, allowing users to feel virtual objects and interactions more convincingly.
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning
- Personalized Experiences: AI and machine learning will enable more personalized and adaptive VR, AR, and XR experiences. These technologies can analyze user behavior and preferences to create tailored content and interactions.
- Smart Environments: AI-driven environments will respond dynamically to user actions, making virtual worlds more responsive and interactive. This could include intelligent virtual assistants and adaptive training programs.
- Greater Cross-Platform Integration
- Unified Ecosystems: The future will likely see greater integration of VR, AR, and XR across different platforms and devices, allowing for seamless transitions between virtual and real-world experiences.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based XR solutions will enable more complex and resource-intensive experiences to be streamed to lightweight devices, expanding accessibility and reducing hardware requirements.
- Advancements in Mixed Reality
- Blended Environments: Mixed Reality (MR) technology will continue to evolve, creating more sophisticated experiences where virtual and real-world elements interact seamlessly. This will have applications in areas like remote collaboration, design, and training.
- Enhanced Immersion and Interactivity
Potential Societal Impacts
- How These Technologies Might Shape Education, Work, Healthcare, and Entertainment
- Education
- Transformative Learning: VR and AR will further revolutionize education by creating highly interactive and immersive learning environments. Virtual classrooms and labs will become more common, enabling students to explore complex concepts and engage in experiential learning.
- Remote Learning: The use of XR for remote education will provide students with virtual access to global resources and expert instructors, bridging gaps in access and quality.
- Work
- Remote Collaboration: XR technologies will enhance remote work by providing virtual meeting spaces where team members can collaborate as if they were physically present. This will improve communication and productivity for distributed teams.
- Training and Simulation: XR will be widely used for training and simulation, allowing employees to practice skills and scenarios in a controlled virtual environment. This will reduce training costs and improve safety and effectiveness.
- Healthcare
- Enhanced Treatments: VR and AR will continue to advance therapeutic treatments, including pain management, mental health therapies, and rehabilitation. These technologies will provide more effective and personalized healthcare solutions.
- Medical Training: XR will improve medical training by offering realistic simulations and interactive learning tools, helping healthcare professionals gain practical experience and skills.
- Entertainment
- Immersive Experiences: The entertainment industry will see further innovations in VR gaming, interactive films, and immersive experiences. Users will be able to engage with content in new and dynamic ways, creating more personalized and engaging experiences.
- Social Interaction: XR will transform social interactions by enabling users to connect and interact in virtual environments, making it easier to share experiences and collaborate with others.
- Education
Challenges and Opportunities
- Ethical Considerations
- Privacy and Security: As XR technologies collect and analyze personal data, ensuring user privacy and data security will be crucial. Ethical practices and regulations will need to be established to protect user information.
- Content Moderation: The immersive nature of XR raises concerns about content moderation and the potential for harmful or inappropriate content. Developing effective content guidelines and moderation tools will be essential.
- Accessibility
- Cost and Availability: The high cost of advanced XR devices may limit accessibility for some users. Efforts to reduce costs and increase availability will be important for broader adoption.
- Inclusive Design: Ensuring that XR experiences are accessible to users with disabilities and diverse needs will be a key challenge. Designing inclusive and adaptable experiences will promote equity and inclusion.
- Potential for Widespread Adoption
- Integration into Daily Life: As XR technologies become more affordable and user-friendly, they will increasingly be integrated into everyday life. This could include applications in home automation, personal health management, and daily tasks.
- Economic Opportunities: The growth of the XR industry will create new economic opportunities, including job creation, entrepreneurial ventures, and investment in related technologies. Embracing these opportunities will drive innovation and growth in the sector.
This section explores the future of VR, AR, and XR, highlighting emerging trends, potential societal impacts, and the challenges and opportunities associated with these technologies. It provides a forward-looking perspective on how these technologies might evolve and shape various aspects of life and industry.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
- Importance and Potential of VR, AR, and XR
- Transformative Impact: Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Extended Reality (XR) are revolutionizing various aspects of our lives by enhancing how we experience entertainment, education, healthcare, and work. These technologies offer immersive and interactive experiences that bridge the gap between the digital and physical worlds.
- Technological Advancements: The evolution of VR, AR, and XR has been marked by significant advancements in hardware and software, leading to more realistic, engaging, and practical applications. From high-resolution VR headsets to sophisticated AR glasses and versatile XR devices, these technologies are becoming more accessible and impactful.
- Practical Applications: The diverse applications of VR, AR, and XR across industries—such as virtual surgeries in healthcare, immersive learning environments in education, interactive retail experiences, and advanced gaming and entertainment—demonstrate their potential to enhance and transform everyday activities and professional practices.
- Future Trends: Emerging trends in VR, AR, and XR, including enhanced immersion, AI integration, and greater cross-platform integration, promise to drive further innovation and expand the scope of these technologies. Their potential societal impacts are profound, shaping how we learn, work, and interact with the world.
Call to Action
- Explore and Engage with Technologies
- Getting Started: We encourage readers to explore VR, AR, and XR technologies, regardless of their technical background. Many devices and applications are now accessible to consumers, and exploring these can provide valuable insights into their potential and applications.
- Educational Resources: Take advantage of online resources, tutorials, and workshops to learn more about VR, AR, and XR. Engaging with these technologies can enhance personal and professional skills and open up new opportunities for creativity and innovation.
- Participate in Social Good Initiatives
- MEDA Foundation’s Mission: We invite you to participate in initiatives that leverage VR, AR, and XR for social good. At the MEDA Foundation, we are committed to using these technologies to support individuals on the autism spectrum and promote self-sufficiency and happiness.
- Contributions and Support: Consider contributing to the MEDA Foundation to support our efforts in creating self-sustaining ecosystems and helping individuals in need. Your participation can make a significant difference in our mission to create a more inclusive and supportive society.
Book References
- “Virtual Reality: Concepts and Technologies” by Philippe Fuchs, Rébecca Baccini, and Jannick Pien
- Provides a comprehensive overview of VR technology, including its history, development, and applications.
- “Augmented Reality: Principles and Practice” by Dieter Schmalstieg and Tobias Hollerer
- Offers an in-depth exploration of AR technology, including its principles, development, and practical applications.
- “Extended Reality: Concepts, Technologies, and Applications” by John S. Gero and Mary Lou Maher
- Discusses the broader spectrum of XR technologies, including VR, AR, and MR, and their potential applications across various fields.










